Table of Contents
- What are some current common uses of digital healthcare solutions?
- In what additional ways can forward-thinking organizations implement digital healthcare?
- What are the requirements for connectivity to support digital healthcare?
- What are some available options for connectivity?
- What steps should healthcare organizations take to improve their connectivity for digital healthcare solutions?
In an increasingly competitive and pressure-filled landscape, healthcare organizations seek to improve both operational efficiency and patient outcomes. Digital healthcare has been a key development in this area, with new technologies constantly arising to support improved care. Digital healthcare technology can help improve access and personalization while reducing inefficiencies and costs, making such technology a necessity for modern healthcare organizations.
But it’s not enough simply to implement new solutions. Improved connectivity is crucial to enable the most effective use of these technologies. The right network infrastructure, combined with best practices for maintenance, can support a positive experience for patients, families, and providers, yielding better care and improved outcomes.
What are some current common uses of digital healthcare solutions?
To understand what’s needed in terms of connectivity, it’s helpful to understand how digital solutions are being used for healthcare, such as:
- Electronic medical records
- Telehealth/telemedicine
- Smart medical devices, including wearable technology for remote patient monitoring
- Asset management, such as tracking where medical devices are located and whether they’re in use
- Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), a subset of IoT that uses sensors and actuators specifically for medical applications, such as asset tracking or data collection from medical devices
- Data analytics, including population health management to spot trends and patterns, such as for infectious disease tracking
None of these solutions operates in a completely contained manner. Patient outcomes depend on having up-to-date information readily available. Thus, these applications require the secure transmission, processing, storage, and retrieval of substantial amounts of data whenever and wherever care happens.
In what additional ways can forward-thinking organizations implement digital healthcare?
Organizations looking for new ways to improve patient care are beginning to implement many innovative solutions, including:
- Medication management uses apps, wearables, and automated dispensers to encourage patients to follow their prescribed regimen.
- Predictive analytics goes beyond analyzing data for past trends to discern patterns with potential future impact – for example, when and where a disease outbreak may be imminent, or when a patient is at risk of an escalating health condition.
- Enhanced imaging and diagnostics use AI algorithms trained on existing data to analyze medical images and other health-related data to aid healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions.
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) – for example, for surgical training – allow medical professionals to learn and practice in a risk-free environment using simulations before working with actual patients.
- Blockchain uses complex codes and transparent, decentralized data logs to improve data security. Despite the strict requirements for the security and privacy of medical data, hundreds of breaches occur yearly in healthcare organizations. Blockchain technology can be useful for digital healthcare, keeping data secure and private while maintaining accessibility for providers and patients.
All these applications require the transmission and processing of vast amounts of real-time data, with the connectivity to support such functions.
What are the requirements for connectivity to support digital healthcare?
Modern healthcare is connected healthcare – for these and other applications, there is a need to transmit a great deal of data on demand. Networks must be able to deliver on these connectivity requirements:
- Reliability – Digital healthcare applications require high reliability to ensure continuous access to critical data and services such as real-time monitoring.
- Low latency – For real-time communication, such as required for telehealth and remote monitoring, low latency is a necessity.
- Scalability – The volume of healthcare data continues to grow exponentially. Your connectivity solution must be scalable to accommodate this growth.
- Interoperability – For various systems, data, and applications to communicate with each other, interoperability is vital. Using standards-based communication protocols and Application Protocol Interfaces (APIs) will provide a solid foundation for interoperability.
- Security – Healthcare data is sensitive, private, and highly regulated; thus, security is paramount. This should include encryption, authentication, network separation (such as with virtual networks), and secure communication protocols to preserve privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
- Regulatory compliance – Aside from supporting basic network security measures, connectivity solutions must comply with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR to ensure that patient data is handled securely.
- Accessibility – As applications such as telehealth and remote monitoring become more widely used, it’s essential to implement connectivity solutions that support remote accessibility. This enables better communication between patients and providers and also enables providers to access patient records from wherever they practice.
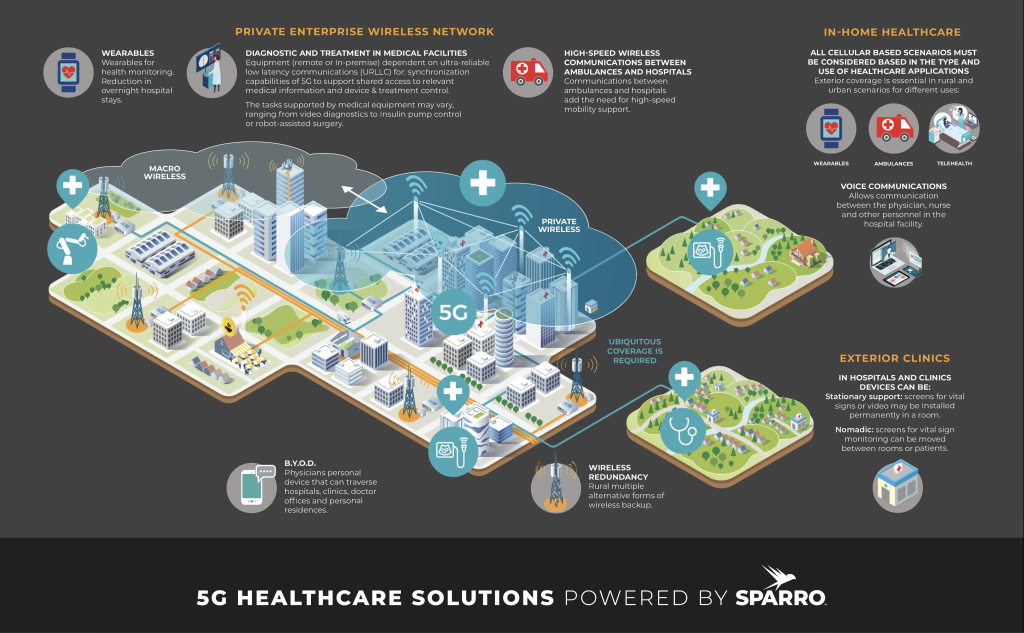
What are some available options for connectivity?
Several options are available to meet the requirements mentioned above. The best solution to support your organization’s digital healthcare solutions will likely incorporate more than one of these options:
- WiFi – A fast, reliable WiFi network provides basic connectivity for providers, patients, and others. It can also support communication among digital healthcare solutions and is especially suited for mobile communications. Properly designed, a WiFi network will cover your entire campus and separate secure/private communications from guest/public communications.
- Other wireless technologies – Technologies such as Bluetooth, Zigbee, and ISA100 Wireless typically connect devices over short distances. They are designed to support networks with many devices and low latency, as IoMT requires.
- Wired connections – Wired technology such as Ethernet and fiber is beneficial for longer-distance connections, as well as those that prioritize security and stability over mobility. Wired networks can also offer redundancy for critical services and solutions. Optical fiber is especially useful for digital healthcare applications due to its high capacity, improved security, and lack of interference with nearby equipment.
- Private 5G networks – The use of private 5G is growing in healthcare, with more than a dozen private 5G networks being announced in the past year. The key benefit here is enterprise-level security, which is a requirement for sensitive and protected medical information. This, combined with enhanced connectivity, low latency, and support for a vast number of devices,
What steps should healthcare organizations take to improve their connectivity for digital healthcare solutions?
As your IT staff will attest, improving connectivity for a complex enterprise such as a healthcare organization isn’t simply a matter of installing WiFi off-the-shelf. There are several important steps you can take to ensure that your network will properly support your digital healthcare initiatives:
- Conduct a connectivity assessment – Look at your current infrastructure and connectivity.
- What digital healthcare solutions are you currently using? What do you plan to add in the coming years?
- Do you have enough capacity/bandwidth to accommodate those solutions?
- Is your current network reliable and accessible? Where are the dead spots?
- Where are the potential bottlenecks?
- Can your current infrastructure support all the digital devices and equipment you need, as well as the increasing collaboration among providers?
- Is your network resilient in the case of outages?
- Make sure you have a high-speed Internet connection with sufficient capacity – Real-time applications require fast, reliable connectivity, typically with a sizable traffic capacity to accommodate large amounts of data.
- Implement both wired and wireless technology – A combination of wired and wireless technology will result in a network that is more flexible and resilient.
- Prioritize cybersecurity – VPNs and other secure communications protocols can help you safeguard patient information and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. Firewalls, intrusion detection solutions, and regular security audits are also crucial.
- Consider a private 5G network – The high speeds, low latency, and enhanced security offered by private 5G make it a good candidate for digital healthcare networks.
- Implement cloud and edge computing – Cloud-based solutions offer scalability to support the growing amount of healthcare data. They also support collaboration among providers. Edge computing, which processes data closer to the source, can support low-latency applications such as real-time diagnostics.
- Ensure interoperability – By using standardized communication protocols and APIs, you can ensure interoperability among multiple providers, device manufacturers, and vendors.
- Conduct regular upgrades – Upgrades to software, firmware, and equipment will not only keep you up to date with technological advancements. They will also ensure you have the latest security features and that your network can support next-generation digital healthcare solutions.
If you’re looking to future-proof your connectivity to support digital healthcare, Sparro can help. We orchestrate the digital transformation of enterprise customers through network infrastructure improvements, private 5G networks, adaptive and autonomous networking, edge computing, IT agility, and connected security. We design your custom solution for easy installation, maintenance, monitoring, and management to simplify the path to deployment and use.

